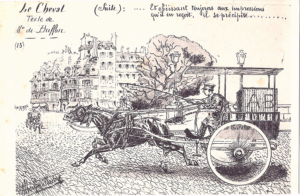
Northern Lights phenomenon - how and why does it happen?

Reverse side of the postcard.
More information
Northern Lights phenomenon - how and why does it happen?
The Northern Lights are photons (light particles) created by the reaction between Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs) and oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the earth’s atmosphere.
The sun hurls out SEPs in solar flares during periods of solar activity. Most of these particles are deflected by the earth’s magnetic field – but the field is weaker in the areas surrounding the North and the South poles and some solar particles make it through the the earth’s atmosphere. Those that do collide with oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the upper atmosphere.
Although the earth’s magnetic field is weaker at the poles, it can also be affected by geomagnetic storms that are caused by solar wind shock waves. Geomagnetic storms have the effect of amplifying the aurora and increasing its visibility.
Object data
Title
Northern Lights phenomenon - how and why does it happen?
Artist
Ljósmyndakompanýið.
Founder
Útgefandi Photo Company.
Date
2014.
Culture
Iceland.
Classification
Postcard.